Are Your Organic Products Authentic? Common Questions Answered
What Does «Organic» Really Mean?
The term «organic» is often thrown around in the food and product industry, but what does it truly mean? Organic products are grown and produced using methods that avoid the use of synthetic pesticides, herbicides, fertilizers, and genetically modified organisms (GMOs). This focus on natural processes ensures that the end product is free from harmful chemicals and residues.
The «organic» label is regulated by various organizations, such as the USDA in the United States, ensuring that producers adhere to strict standards. These regulations cover various aspects, including soil health, pest control, animal welfare, and food processing. These guidelines aim to minimize environmental impact and promote sustainable agricultural practices.
Consumers often associate organic products with a healthier lifestyle and a reduced environmental footprint. They believe that organic foods are safer and more nutritious than conventionally grown counterparts. However, it’s important to note that scientific evidence on the nutritional superiority of organic foods remains inconclusive.
While organic farming practices can contribute to soil health and biodiversity, they may not always be the most efficient method in terms of yield. Therefore, choosing organic products often comes with a higher price tag due to the extra labor and resources required to adhere to organic standards.
Ultimately, the decision to buy organic is a personal one. It’s important to understand the principles behind organic production, weigh the benefits and drawbacks, and make an informed choice based on your values and priorities.
For those who prioritize environmental sustainability, animal welfare, and reduced chemical exposure, organic products offer a compelling choice. For others, cost and efficiency may be more significant considerations. Regardless of your personal stance, understanding the meaning of «organic» can empower you to make more informed decisions about the products you consume.

How Can I Be Sure My Organic Products Are Authentic?
In a world where authenticity can be questioned, it’s understandable to wonder how you can be sure your organic products are genuinely organic. Fortunately, there are several ways to ensure you’re getting the real deal:
Look for Certification Labels: The most reliable way to verify organic products is by checking for certification labels. These labels, issued by independent organizations, signify that the product has met specific organic standards. In the United States, the USDA Organic seal is a widely recognized and trusted certification. Other reputable certifications include those from organizations like the Organic Trade Association (OTA) and the California Certified Organic Farmers (CCOF).
Read the Labels Carefully: Pay close attention to the ingredients list and any claims made on the product packaging. Organic ingredients should be clearly stated, and the label should indicate that the product is certified organic. Beware of products that use vague or misleading terms like «natural» or «organic-like» as these might not meet strict organic standards.
Shop from Reputable Sources: Opt for shopping at trusted farmers’ markets, co-ops, or stores that specialize in organic products. These retailers often have a strong commitment to organic practices and source their goods from certified suppliers. You can also inquire about their sourcing practices to gain greater assurance.
Research the Brand: Take the time to research the brand behind the product. Many organic brands have websites or social media pages that share their commitment to organic practices and provide information about their certification process. Look for transparency and evidence of their commitment to organic principles.
Ask Questions: Don’t hesitate to ask questions about the product’s origin, certification, and growing methods. Retailers and producers should be able to provide detailed information about their organic practices. If you’re unsure, it’s always a good idea to seek information from a trusted source.
By taking these steps, you can increase your confidence in the authenticity of your organic products. Remember, supporting organic producers not only benefits your health and the environment but also promotes sustainable agricultural practices for generations to come.

Are Organic Products More Expensive Than Conventional Products?
The price difference between organic and conventional products is a common concern for consumers. While it’s true that organic products often come with a higher price tag, there are several reasons behind this difference.
Higher Production Costs: Organic farming practices typically require more labor and resources compared to conventional methods. Organic farmers use natural fertilizers and pest control techniques, which can be more time-consuming and less efficient than their synthetic counterparts. Additionally, organic farmers face stricter regulations and inspections, which contribute to higher production costs.
Demand and Supply: The demand for organic products has been steadily increasing in recent years, leading to higher prices. However, the supply of organic products often lags behind demand, contributing to market fluctuations and increased costs.
Consumer Preferences: Consumers who choose organic products are willing to pay a premium for the perceived benefits, such as health, environment, and animal welfare. This willingness to pay a higher price drives up demand and influences pricing.
Transportation and Distribution: Organic products often travel longer distances to reach consumers, which can contribute to higher transportation costs. Additionally, distribution networks for organic products may be less efficient than those for conventional products, further impacting costs.
Brand and Marketing: Organic brands often invest more in marketing and branding to communicate the value proposition of their products. These marketing efforts can contribute to higher prices, as consumers associate the brands with quality and sustainability.
While the price difference between organic and conventional products can be significant, it’s important to remember that organic farming supports sustainable practices, promotes environmental health, and prioritizes animal welfare. If you’re concerned about the cost, consider purchasing organic products in season, taking advantage of sales and promotions, or buying in bulk.
Ultimately, the decision to purchase organic products comes down to personal priorities and affordability. While the higher cost might be a factor for some, others might be willing to pay a premium for the added value and benefits associated with organic production.

Are Organic Products Really Healthier Than Conventional Products?
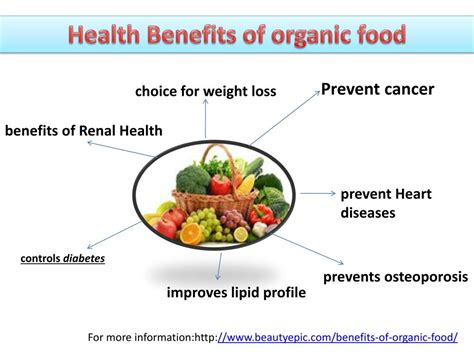
The question of whether organic products are truly healthier than their conventional counterparts is a complex and hotly debated topic. While there is no conclusive scientific evidence to prove that organic foods are inherently more nutritious, some studies suggest potential benefits.
Lower Pesticide Residues: Organic farming practices prohibit the use of synthetic pesticides, herbicides, and fertilizers, leading to lower levels of pesticide residues in organic products. This reduced exposure to chemicals is often cited as a health benefit of organic food.
Higher Levels of Certain Nutrients: Some studies have shown that organic fruits and vegetables may contain higher levels of certain nutrients, such as antioxidants and vitamins. However, the differences in nutrient content between organic and conventional products are often small and inconsistent.
Animal Welfare: Organic livestock farming emphasizes animal welfare by prohibiting the use of antibiotics and hormones. Organic animals are often raised on pasture and given access to outdoor space, which can improve their overall health and well-being.
Environmental Sustainability: Organic farming practices prioritize soil health, biodiversity, and water conservation, contributing to a more sustainable food system. These environmental benefits can indirectly impact human health by promoting clean air, water, and food.
Limited Evidence: It’s important to note that the research on the health benefits of organic foods is still evolving. While some studies suggest potential advantages, others have not found significant differences between organic and conventional products. Furthermore, the health benefits of organic food may vary depending on factors like the type of product, growing conditions, and geographical location.
Individual Choices: Ultimately, the decision to choose organic products is a personal one based on individual preferences and values. Some consumers may prioritize reduced chemical exposure and animal welfare, while others may focus on environmental sustainability. Regardless of your motivation, it’s essential to make informed choices based on reliable information and scientific evidence.
While organic products may not always be proven to be more nutritious, the potential benefits in terms of reduced pesticide residues, animal welfare, and environmental sustainability make them a compelling choice for many consumers.
Are Organic Products Safe for Everyone?
While organic products are generally considered safe for most individuals, there are some considerations to keep in mind. Here are some potential safety concerns:
Allergies: Organic products, just like conventional ones, can contain allergens. People with allergies to specific ingredients, such as nuts, gluten, or dairy, should always check the labels carefully to ensure the products are safe for consumption. It’s also important to be aware of potential cross-contamination in processing facilities, particularly for people with severe allergies.
Contamination: Organic foods can still be subject to contamination from bacteria, viruses, or parasites. Proper food handling and preparation practices are essential to minimize the risk of foodborne illness, regardless of whether the product is organic or conventional. This includes thorough washing, cooking to safe temperatures, and storing foods properly.
Nutrient Deficiencies: Some studies suggest that organic foods may have lower levels of certain nutrients compared to conventionally grown foods. However, these differences are often small and inconsistent, and a balanced diet should provide adequate nutrients, regardless of the source of food.
Cost: The higher cost of organic products can be a barrier for some individuals, particularly those on a tight budget. If you’re concerned about cost, consider purchasing organic products in season, taking advantage of sales and promotions, or buying in bulk.
Environmental Impact: While organic farming practices are generally more sustainable than conventional methods, they can still have an environmental impact. For example, organic farming requires more land to produce the same amount of food as conventional farming. Therefore, it’s important to consider the full environmental impact of your food choices, including transportation, packaging, and waste.
In conclusion, organic products are generally safe for most individuals. However, it’s essential to be aware of potential safety concerns, including allergies, contamination, nutrient deficiencies, cost, and environmental impact. Make informed choices based on your individual needs and preferences, and consult with healthcare professionals if you have any concerns.

How Can I Reduce My Exposure to Pesticides in Food?
While organic farming eliminates the use of synthetic pesticides, it’s important to note that pesticide residues can still be found in conventional produce. Here are some tips to reduce your exposure to pesticides in your food:
- Choose Organic: Opting for organic produce significantly reduces your exposure to pesticides. Look for the USDA Organic seal or other reputable certifications.
- Wash Your Produce Thoroughly: Even organic produce can be exposed to pesticides from the environment. Wash fruits and vegetables thoroughly with water before consumption to remove any remaining residue.
- Peel Your Produce: When possible, peel fruits and vegetables to remove the outer layer, where pesticide residues are often concentrated. This is particularly beneficial for fruits and vegetables with waxy exteriors.
- Eat a Variety of Foods: Include a diverse range of fruits, vegetables, grains, and other food sources in your diet to minimize your exposure to specific pesticides. A varied diet helps to balance out any potential risks from pesticide residues.
- Buy from Local Farmers: Supporting local farmers who practice sustainable farming methods, including organic farming, can help reduce your exposure to pesticides.
- Cook Your Food: Cooking food can destroy some pesticide residues. However, it’s important to note that some pesticides may be heat-resistant.
- Consider the «Dirty Dozen» and «Clean Fifteen»: The Environmental Working Group (EWG) publishes annual lists of the «Dirty Dozen,» which are fruits and vegetables with the highest pesticide residues, and the «Clean Fifteen,» which are fruits and vegetables with the lowest pesticide residues. This information can help you make informed choices when selecting produce.
Remember, even with these tips, it’s impossible to eliminate all pesticide exposure from your diet. However, by taking these steps, you can significantly reduce your exposure and promote a healthier lifestyle.
What are the Environmental Benefits of Organic Farming?
Organic farming practices go beyond avoiding synthetic chemicals; they actively promote environmental sustainability. Here are some key environmental benefits of organic farming:
- Soil Health: Organic farming practices focus on building healthy soil through the use of compost, cover crops, and crop rotation. Healthy soil improves water retention, reduces erosion, and enhances nutrient cycling.
- Biodiversity: Organic farms provide habitat for a wider variety of plants, animals, and insects, contributing to biodiversity and ecosystem health. This supports pollination, natural pest control, and healthy soil ecosystems.
- Water Conservation: Organic farming practices, such as using cover crops and reducing tillage, help conserve water by minimizing evaporation and runoff. These techniques promote water infiltration and soil moisture retention.
- Reduced Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Organic farming practices contribute to lower greenhouse gas emissions compared to conventional agriculture. This is primarily due to the reduced use of synthetic fertilizers, which produce significant emissions during production and application.
- Improved Water Quality: Organic farming practices reduce pollution of water bodies by minimizing the use of synthetic fertilizers and pesticides, which can contaminate groundwater and surface water.
These environmental benefits highlight the importance of supporting organic farming practices. By choosing organic products, consumers can contribute to a more sustainable food system and protect the environment for future generations.
Can I Grow My Own Organic Food?
Growing your own organic food is a rewarding and empowering way to control your food sources, reduce your environmental impact, and enjoy fresh, wholesome produce. While it might seem daunting, growing your own food can be a surprisingly easy and enjoyable experience.
Here’s a step-by-step guide to get you started:
- Choose a Suitable Location: Select a sunny spot in your yard or garden with well-drained soil. The amount of space you have will determine the type and amount of food you can grow.
- Prepare the Soil: Test your soil to determine its pH and nutrient levels. Amend the soil with compost, manure, or other organic materials to improve fertility and drainage. Remove weeds and any existing plants.
- Select Your Crops: Choose vegetables, fruits, or herbs that thrive in your climate and soil conditions. Start with easy-to-grow options, such as tomatoes, peppers, lettuce, or herbs.
- Plant Your Seeds or Seedlings: Follow the planting instructions for each crop. Space your plants appropriately to allow for growth and air circulation. Water your plants regularly, ensuring the soil is consistently moist.
- Control Pests and Diseases: Use organic pest control methods, such as hand-picking pests, using insecticidal soap, or attracting beneficial insects. Monitor your plants for signs of disease and take appropriate action.
- Harvest Your Produce: Enjoy the fruits of your labor! Harvest your crops at the optimal time for maximum flavor and freshness. Learn about the different stages of maturity for each crop to ensure you harvest at the right time.
Growing your own organic food is a rewarding and sustainable way to connect with nature, enjoy fresh, healthy food, and make a positive impact on the environment.
What are the Ethical Considerations of Organic Farming?
Organic farming is not only about avoiding synthetic chemicals and promoting environmental sustainability, but also about ethical considerations that extend to animal welfare and fair labor practices.
Animal Welfare: Organic livestock farming prioritizes animal welfare, prohibiting the use of antibiotics and hormones for growth. Organic animals are often raised on pasture and given access to outdoor space, promoting their natural behaviors and improving their overall health and well-being.
Fair Labor Practices: Organic farming often emphasizes fair labor practices, promoting fair wages, safe working conditions, and worker empowerment. Supporting organic farms that adhere to these principles helps to ensure ethical treatment of farm workers.
Transparency and Traceability: Organic certification programs often require producers to maintain transparent records and traceability systems. This ensures that consumers can track the origin of their food and be confident in the ethical practices used throughout the production process.
By considering these ethical factors, consumers can make informed choices that support organic farms that prioritize animal welfare, fair labor practices, and responsible sourcing.
Is Organic Farming Always Sustainable?
While organic farming practices generally promote sustainability, there are certain aspects to consider.
Land Use: Organic farming often requires more land to produce the same amount of food compared to conventional agriculture. This is due to lower yields and the need for crop rotation and fallow periods. Therefore, the environmental impact of organic farming can be influenced by land-use efficiency.
Water Use: Organic farming can be water-intensive, especially in arid regions. It’s important to consider local water availability and implement water-conservation practices when choosing organic farming methods.
Transportation: Organic products may travel longer distances to reach consumers, contributing to higher transportation costs and emissions. Supporting local organic producers can minimize transportation impacts.
Certification Costs: Organic certification can be expensive, making it challenging for small farmers to participate. This can limit the availability of organic products and potentially disadvantage smaller farms.
While organic farming is generally considered more sustainable than conventional agriculture, it’s important to consider the full environmental and economic aspects. Choosing organic products from local producers and supporting initiatives that promote sustainable organic farming practices can help mitigate these challenges.

Summary Table
| Topic | Benefits of Organic | Challenges of Organic |
|---|---|---|
| Health | Lower pesticide residues, potentially higher nutrient levels | Limited scientific evidence on superior nutrition, potential for contamination |
| Environment | Improved soil health, biodiversity, water conservation, reduced greenhouse gas emissions | Higher land use, potentially higher water use, transportation impacts |
| Ethics | Animal welfare, fair labor practices, transparency and traceability | Certification costs can be challenging for small farms |
| Cost | May be more expensive than conventional products | Higher costs can be a barrier for some consumers |
FAQ
Are organic products always better than conventional products?
There is no one-size-fits-all answer. Organic products offer benefits in terms of reduced chemical exposure, animal welfare, and environmental sustainability. However, conventional products may be more affordable and readily available. Ultimately, the choice depends on individual priorities and values.
What if I can’t afford organic products?
Consider purchasing organic products in season when they are more affordable. Look for sales and promotions. You can also buy in bulk to save money. Prioritize organic products for items you consume frequently, such as fruits, vegetables, and meats, and choose conventional options for items you consume less often.
Are organic products always pesticide-free?
Organic farming prohibits the use of synthetic pesticides, but organic products can still be exposed to pesticides from the environment. Washing your produce thoroughly is essential, regardless of whether it is organic or conventional.
Can I trust the organic label?
Look for reputable certifications, such as the USDA Organic seal. Certified organic products have met specific standards and undergone inspections to ensure authenticity.
How do I know if an organic farm is ethical?
Research the farm’s practices and look for certifications that address animal welfare and fair labor practices. You can also inquire about their ethical sourcing and transparency policies.
Can I grow my own organic food without a garden?
Yes, you can grow your own organic food in containers or vertical gardens. Many herbs, leafy greens, and vegetables can thrive in pots or raised beds. Consider starting small with easy-to-grow options.
Are organic products healthier for children?
While there is no conclusive evidence that organic products are inherently healthier for children, reducing exposure to pesticides and promoting a diet rich in fruits and vegetables is generally beneficial. A balanced diet, including organic options when possible, is key to supporting children’s health and well-being.
